Impacts of irrigation development on water quality in the San Salvador watershed (Part 1)
Assessment of current nutrient delivery and transport using SWAT
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31285/AGRO.27.1198Keywords:
sustainable agriculture, water quality, SWATAbstract
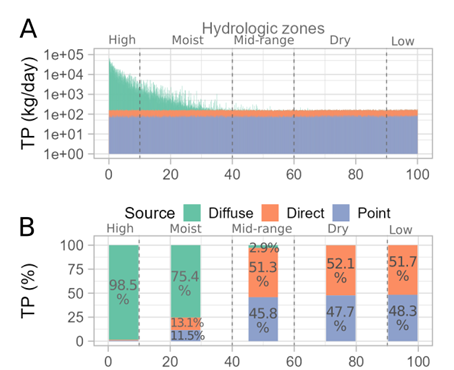
The development of irrigation involves a change in land use and management and has implications for water quality and quantity. It is critical to design conservation practices and best management practices consistent with sustainable agricultural intensification. The objective of this work was to understand and characterize key processes affecting hydrology, nutrient export and transport, and quantify impacts in the San Salvador watershed. For such purpose, the Soil & Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) was implemented, calibrated for water quantity, and water quality was adjusted using soft calibration techniques. The model reproduces water quantity and nutrient balance, and aids in characterizing the nutrient delivery and transport in the watershed. The magnitude of runoff affects the balance of nutrients. In high flows, diffuse sources are more prevalent, while in low flows, point sources and direct livestock manure to the river are more significant. The main outcomes of this work contribute to the design of strategies to achieve sustainable agricultural intensification. It also describes a new modeling tool freely available that could be used in further studies.
Downloads
References
Abbaspour KC, Johnson CA, van Genuchten MTh. Estimating uncertain flow and transport parameters using a sequential uncertainty fitting procedure. Vadose Zone J. 2004;3(4):134052. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2113/3.4.1340
Abbaspour KC, Rouholahnejad E, Vaghefi S, Srinivasan R, Yang H, Kløve B. A continental-scale hydrology and water quality model for Europe: calibration and uncertainty of a high-resolution large-scale SWAT model. J Hydrol. 2015;524:73352. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.03.027
Arnold JG, Srinivasan R, Muttiah RS, Williams JR. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part I: model development. J Am Water Resour Assoc. 1998;34(1):73-89. Doi: 10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb05961.x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb05961.x
Arnold JG, Youssef MA, Yen H, White MJ, Sheshukov AY, Sadeghi AM, MoriasiAM,Steiner JL, Amatya D, Skaggs RW, Haney EB, JeongJ, ArabiM,Gowda PH.Hydrological processes and model representation: impact of soft data on calibration. Trans ASABE. 2015;58(6):1637-60. DOI: https://doi.org/10.13031/trans.58.10726
Aubriot L, Chalar G, De León L, Goyenola G, Lizarralde C, Míguez B, PerdomoC, QuintansF, RodóE, Teixeira de Mello F. Establecimiento de niveles guía de estado trófico en cuerpos de agua superficiales. Montevideo:MA; 2017. 48p.
Aznarez C, Jimeno-Sáez P, López-Ballesteros A, Pacheco JP, Senent-Aparicio J. Analysing the impact of climate change on hydrological ecosystem services in Laguna del Sauce (Uruguay) using the SWAT Model and Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens (Basel). 2021;13(10):2014. Doi: 10.3390/rs13102014. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13102014
Brirhet H, Benaabidate L. Comparison of two hydrological models (Lumped And Distributed) over a pilot area of the Issen Watershed In The Souss Basin, Morocco. Eur Sci J. 2016;12(18):347.Doi: 10.19044/esj.2016.v12n18p347. DOI: https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2016.v12n18p347
Brown L, Barnwell T. The Enhanced Stream Water Quality Models QUAL2E and QUAL2E-UNCAS (EPA/600/3-87-007). Athens: Environmental Research Laboratory; 1987.188p.
Calvo C. Rol ecosistémico de la zona riparia en sistemas dulceacuícolas en un escenario de cambio global[doctoral’s thesis]. Montevideo (UY): Universidad de la República, Facultad de Agronomía;2022.146p.
Clericci C, Préchac F. Aplicaciones del modelo USLE/RUSLE para estimar pérdidas de suelo por erosión en Uruguay y la región sur de la cuenca del Río de la Plata. Agrociencia. 2001;5(1):92-103.
Climate-Smart Agriculture in Uruguay [Internet]. Washington: The World Bank Group; 2015 [cited 2023 Dec 04].Available from: https://climateknowledgeportal.worldbank.org/sites/default/files/2019-06/CSA%20in%20Uruguay.pdf
Durán A. Clasificación hidrologica de los suelos del Uruguay. Agrociencia Uruguay 1997;1(1):15-29.Doi: 10.31285/AGRO.01.1009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31285/AGRO.01.1009
García JA. Producción de forraje de pasturas cultivadas en la Región Litoral Sur. In: Risso D, Berretta E, Morón A, editors. Producción y manejo de pasturas. Montevideo: INIA; 1996. pp.163-8.
Gelós M, Neighbur N, Kok P, Badano L, Hastings F, Nervi E,Alonso J, Navas R, Vervoort W, Baethgen W. On the prediction of phosphorus fluxes in the Santa Lucía basin under different land use and management practices using SWAT model. In:Phosphorus in Soils and Plants Symposium towards a sustainable phosphorus utilization in agroecosystems.Montevideo: Facultad de Agronomía; 2022. pp. 81.
Genta JL, Failache N, Alonso J, Bellón D. Balances hídricos superficiales en cuencas del Uruguay. Montevideo: Universidad de la República; 2001.115p.
Gorgoglione A, Gregorio J, Ríos A, Alonso J, Chreties C, Fossati M. Influence of Land Use/Land Cover on Surface-Water Quality of Santa Lucía River, Uruguay. Sustainability. 2020;12(11):4692.Doi: 10.3390/su12114692. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114692
Gorgoglione A, Silveira L, Eguren G, Rivas N, Hastings F, Saracho A, Rosas F, Pérez A, Basile F, Carriquiry M, Tiscornia G, Cal A, Navas R, García C, Otero A, Roel A, Vilaseca F, Rodriguez R, Pastorini M, Chreties C, Alonso J, Baethgen W,AncevT, Vervoot RW, Nervi E, Rosas F. Plataforma para el soporte a la toma de decisión en el desarrollo de la agricultura irrigada sostenible (DAIS-STD)[Internet].[Place unknown]: OSF;2023 [cited 2023 Dec 18]. Available from: https://osf.io/ytn9g/
Gupta HV, Kling H, Yilmaz KK, Martinez GF. Decomposition of the mean squared error and NSE performance criteria: implications for improving hydrological modelling. J Hydrol. 2009;377(1-2):80-91. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.08.003
Hastings F, Fuentes I, Perez-Bidegain M, Navas R, Gorgoglione A. Land-cover mapping of agricultural areas using machine learning in Google Earth Engine. In: International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications. Cham: Springer;2020.pp. 721-36. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58811-3_52
Hastings F, Kok P, Gelós M, Tejera Á. Implementación de un modelo de calidad de agua con la herramienta SWAT en la cuenca del Río Negro. In: XI Congreso Nacional de AIDIS [Internet]. Montevideo: AIDISUruguay;2022 [cited 2023 Dec 19]. 8p. Available from: https://aidis.org.uy/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Hastings-Florencia.pdf
Hastings F, Perez-Bidegain M, Navas R, Gorgoglione A. Impacts of irrigation development on water quality in the San Salvador watershed (Part 2): implementation of scenarios in SWAT. Agrociencia Uruguay. Agrocienc Urug. 2023;27(NE1):e1199. Doi: 10.31285/AGRO.27.1199. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31285/AGRO.27.1199
Her Y, Frankenberger J, Chaubey I, Srinivasan R. Threshold effects in HRU definition of the soil and water assessment tool. Trans ASABE. 2015;58(2):367-78. DOI: https://doi.org/10.13031/trans.58.10805
Her Y, Yoo SH, Cho J, Hwang S, Jeong J, Seong C. Uncertainty in hydrological analysis of climate change: multi-parameter vs. multi-GCM ensemble predictions. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):4974.Doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41334-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41334-7
Hernández J, Otegui O, Zamalvide JP. Formas y contenidos de fósforo en algunos suelos del Uruguay. Boletín de Investigación. 1995(43):32p.
Infraestructura de datos espaciales[Internet]. Montevideo: IDEuy; [cited 2023 Jul 18]. Available from: https://visualizador.ide.uy/ideuy/core/load_public_project/ideuy/
INIA. Banco de datos agroclimáticos [Internet]. Montevideo: INIA; [cited 2023 Jul 18]. Available from: https://bit.ly/2KOj2dZ
Instituto Nacional de Estadística.Resultados del Censo de Población 2011: población, crecimiento y estructura por sexo y edad. Montevideo: INE; 2012. 17p.
Instituto Uruguayo de Meteorología. Clasificación climática [Internet]. Montevideo: INUMET; [cited 2023 Jul 18].Available from: https://www.inumet.gub.uy/clima/estadisticas-climatologicas/clasificacion-climatica
Kennedy J, Eberhart R. Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN’95 - International Conference on Neural Networks; 1995 Nov 27 – Dec 1; Perth, WA, Australia.Perth:IEEE;1995.pp.1942-8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
Knoben WJM, Freer JE, Woods RA. Inherent benchmark or not? Comparing Nash-Sutcliffe and Kling-Gupta efficiency scores. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci. 2019;23(10):4323-31.Doi: 10.5194/hess-2019-327. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-23-4323-2019
Liu L, Wang QJ, Xu YP. Temporally varied error modelling for improving simulations and quantifying uncertainty. J Hydrol. 2020;586:124914.Doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124914. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124914
Mapa de estaciones del Instituto Uruguayo de Meteorología (INUMET) [Internet]. Montevideo: INUMET;[cited 2023 Jul 18];Available from: https://www.inumet.gub.uy/clima/recursos-hidricos/mapa-de-estaciones
Mer F, Vervoort RW, Baethgen W. Building trust in SWAT model scenarios through a multi-institutional approach in Uruguay. SESMO. 2020;2:17892.Doi: 10.18174/sesmo.2020a17892. DOI: https://doi.org/10.18174/sesmo.2020a17892
Merriman KR, Gitau MW, Chaubey I .A tool for estimating best management practice effectivenessin Arkansas. Appl Eng Agric. 2009;25(2):199-213. DOI: https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.26333
Ministerio de Ambiente, DINAGUA (UY). Visualizadores geográficos de DINAGUA [Internet]. Montevideo: MA; [cited 2023 Jul 18].Available from: https://www.ambiente.gub.uy/informacion_hidrica/
Ministerio de Ganadería, Agricultura y Pesca (UY). Censo General Agropecuario1990. Montevideo: DCE; 1994. 239p.
Ministerio de Ganadería, Agricultura y Pesca (UY). Uruguay agrointeligente: los desafíos para un desarrollo sostenible. Montevideo: MGAP; 2017. 161p.
Ministerio de Ganadería, Agricultura y Pesca, DGRN (UY). Carta de suelos escala1:40,000 [Internet].Montevideo: MGAP; [cited 2023 Jul 18].Available from: https://dgrn.mgap.gub.uy/js/visores/dgrn/#
Ministerio de Ganadería, Agricultura y Pesca, DGRN (UY). Estimación de fósforo index [Internet]. Montevideo: MGAP; 2022[cited 2023 Dec18]. Available from: https://bit.ly/4aM1tCO
Ministerio de Ganadería, Agricultura y Pesca, DIEA (UY).Anuario Estadístico Agropecuario 2021. Montevideo: MGAP; 2022.263p.
Ministerio de Ganadería, Agricultura y Pesca, SNIG (UY). Datos basados en la declaración jurada de existencias [Internet]. Montevideo: MGAP; [cited 2023 Jul 18].Available from:https://www.snig.gub.uy/principal/snig-principal-institucional-indicadores
Ministerio de Vivienda, Ordenamiento Territorial y Medio Ambiente, DINAMA (UY). Evolución de la calidad de agua en la cuenca del río San Salvador: período 2014-2019. Montevideo: MVOTMA; 2020.77p.
Moriasi DN, Arnold JG, Liew MW Van, Bingner RL, Harmel RD, Veith TL. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Trans ASABE. 2007;50(3):885-900. DOI: https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.23153
Nair SS, King KW, Witter JD, Sohngen BL, Fausey NR. Importance of crop yield in calibrating watershed water quality simulation tools1. J Am Water Resour Assoc. 2011;47(6):1285-97. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2011.00570.x
Nash JE, Sutcliffe JV. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I: a discussion of principles. J Hydrol. 1970;10(3):282-90. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(70)90255-6
Neitsch S, Arnold JG, Kiniry JR, Williams JR. Soil and water assessment tool.Temple: Texas A&M University; 2011.618p.
Nelson AM, Moriasi DN, Talebizadeh M, Steiner JL, Gowda PH, Starks PJ, Tadesse HK. Use of soft data for multicriteria calibration and validation of Agricultural Policy Environmental eXtender: impact on model simulations. J Soil Water Conserv. 2018;73(6):623-36. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2489/jswc.73.6.623
Nervi E, Gelós M, Kok P, Alonso J, Navas R, Badano L, Neighbur N, Hastings F, Vervoort RW, Baethgen W. Evaluación de escenarios de uso del suelo en una subcuenca del río Santa Lucía utilizando el modelo SWAT. In: XI Congreso Nacional de AIDIS[Internet]. Montevideo: AIDIS Uruguay; 2022 [cited 2023 Dec 19]. 8p. Available from: https://aidis.org.uy/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Nervi-Eliana-2.pdf
Nossent J, Bauwens W. Multi-variable sensitivity and identifiability analysis for a complex environmental model in view of integrated water quantity and water quality modeling. Water Sci Technol. 2012;65(3):539-49. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2012.884
Osmond DL, Meals DW, Hoag DL, Arabi M, Luloff AE, Jennings GD, McFarland ML, Spooner J, Sharpley AN, Line DE. Synthesizing the experience of the 13 National Institute of Food and Agriculture-Conservation Effects Assessment Project Watershed Studies: present and future. In: Osmond DL, Meals DW, Hoag DLK, Arabi M, editors.How to build better agricultural conservation programs to protect water quality: The National Institute of Food and Agriculture-Conservation Effects Assessment Project Experience. Ankeny:Soil and Water Conservation Society;2012. pp.151-67.
Paudel M, Nelson EJ, Downer CW, Hotchkiss R. Comparing the capability of distributed and lumped hydrologic models for analyzing the effects of land use change. J Hydroinformatics. 2011;13(3):461-73. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2010.100
Pedro A, Macarena C, Cintia P. Análisis del agro-negocio como forma de gestión empresarial en América del Sur: el caso uruguayo. Agrociencia Uruguay. 2012;16(1):110-9.Doi: 10.31285/AGRO.17.546. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31285/AGRO.17.546
Perdomo C. Metodología de estimación de aportes difusos de nitrógeno y fósforo a aguas superficiales desde suelos bajo uso agropecuario. Montevideo: MA; 2013. 6p.
Perdomo C, Barbazán M, Durán JM. Nitrógeno [Internet]. Montevideo: Facultad de Agronomía;[cited 2023 Jul 18]. 70p. Available from: http://www.fagro.edu.uy/fertilidad/publica/Tomo%20N.pdf
Petraglia C, Dell’Acqua M, Pereira G, Yussim E. Mapa integrado de cobertura / uso del suelo del Uruguay, año 2018. In: Anuario OPYPA 2019. Montevideo: MGAP; 2019.pp. 523-31.
Plan de Acción Santa Lucía:medidas de segunda generación. Montevideo:GNA; 2018. 95p.
Sadeghi SHR, Gholami L, Khaledi Darvishan A, Saeidi P. A review of the application of the MUSLE model worldwide. Hydrol Sci J. 2014;59(2):365-75. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2013.866239
Saltelli A, Tarantola S, Chan KPS. A Quantitativemodel-independent method for global sensitivity analysis of model output.Technometrics. 1999;41(1):39-56. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1999.10485594
Saxton KE, Rawls WJ. Soil water characteristic estimates by texture and organic matter for hydrologic solutions. Soil Sci Soc Am J. 2006;70(5):1569-78. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2005.0117
Schuerz C. SWATrunR: Running SWAT2012 and SWAT+ Projects in R. R package version 0.2.7 [Internet]. California: Github; 2019 [cited 2023 Aug 23]. Available from: https://github.com/chrisschuerz/SWATplusR
Seibert J. On the need for benchmarks in hydrological modelling. Hydrol Process. 2001;15(6):1063-4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.446
Sikorska AE, Renard B. Calibrating a hydrological model in stage space to account for rating curve uncertainties: general framework and key challenges. Adv Water Resour. 2017;105:5166. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2017.04.011
Tchobanoglous G, Burton FL; Metcalf & Eddy. Wastewater engineering: treatment, disposal and reuse. New York:McGraw-Hill; 1991. 1334p.
Tomer MD, Sadler EJ, Lizotte RE, Bryant RB, Potter TL, Moore MT, Veith TL, Baffaut C, Locke MA, Walbridge MR.A decade of conservation effects assessment research by the USDA Agricultural Research Service: Progress overview and future outlook. J Soil Water Conserv.2014;69(5):365-73. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2489/jswc.69.5.365
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. An approach for using load duration curves in the development of TMDLs [Internet]. Washington: Watershed Branch;2007[cited 2023 Dec18]. 68p. Availablefrom:https://bit.ly/3TEtjKQ
Ullrich A, Volk M. Application of the Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT) to predict the impact of alternative management practices on water quality and quantity. Agric Water Manag. 2009;96(8):1207-17. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2009.03.010
United States Department of Agriculture, NRCService. Core4 conservation practices training guides: the common sense approach to natural resource conservation. Washington: USDA; 1999. 395p.
Vilaseca F, Castro A, Chreties C, Gorgoglione A. Daily rainfall-runoff modeling at watershed scale: a comparison between physically-based and data-driven models. In: Computational Science and Its Applications – ICCSA 2021. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 2021. pp.18-33. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87007-2_2
White MJ, Arnold JG. Development of a simplistic vegetative filter strip model for sediment and nutrient retention at the field scale. Hydrol Process. 2009;23(11):1602-16. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7291
Williams JR. Sediment yield predictions with universal equation using runoff energy factor. In: Present and prospective technology for predicting sediment yield and sources. Washington: USDA; 1975. pp. 244-52.
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD. Predicting rainfall-erosion losses from cropland east of the Rocky Mountains:guide for selection of practices for soil and water conservation. Washington: USDA; 1965. 47p.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Agrociencia Uruguay

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

















