Evaluación de la dependencia entre el uso/cobertura del suelo y la calidad del agua
comparación entre una cuenca pequeña y una grande en Uruguay
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31285/AGRO.27.1192Palabras clave:
calidad del agua, uso/cobertura del suelo, aprendizaje no supervisado, características relevantesResumen
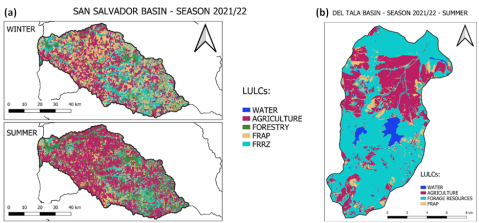
Los cambios en el uso del suelo y la cobertura del suelo (LULC) afectan directa o indirectamente la calidad del agua en cursos de agua y embalses. Las estrategias de gestión sostenible destinadas a mejorar la salud del ecosistema y el bienestar de la comunidad requieren una evaluación precisa de la calidad del agua. Este estudio analiza la correlación entre los cambios temporales en LULC, representados por variables de paisaje seleccionadas (área y proporción de cobertura del suelo, densidad de parches, distancia euclidiana al vecino más cercano, índice de forma promedio e índice de Shannon), y las variables de calidad del agua (nitrato, fósforo total y sólidos suspendidos totales) a nivel de cuenca. Para comparar la influencia del tamaño de la cuenca, este análisis se realizó a dos escalas espaciales diferentes representadas por dos cuencas uruguayas de diferentes tamaños, San Salvador (3118 km2) y Del Tala (160 km2). Se emplearon modelos de aprendizaje automático no supervisados de Mínimos Cuadrados Parciales y Bosque Aleatorio para este análisis. Al aprovechar un método no sesgado basado en teoría de juegos (SHAP), las características de LULC se cuantificaron y clasificaron según su nivel de importancia en la evaluación de la calidad del agua. Los principales resultados de este estudio demostraron que la densidad de parches es una de las métricas más influyentes en ambas cuencas y para ambos modelos. El uso agrícola del suelo es crítico en ambas cuencas, y los usos agrícolas con cultivos forrajeros son los más importantes para ambos algoritmos. Además, es posible afirmar que las técnicas adoptadas son herramientas valiosas que pueden proporcionar una visión adecuada del comportamiento de la calidad del agua en el espacio y el tiempo, así como las correlaciones entre las variables de calidad del agua y LULC.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Amiri BJ, Nakane K. Modeling the linkage between river water quality and landscape metrics in the Chugoku district of Japan. Water Resour Manag. 2009;23(5):931-56.
Arbeletche P, Ernst O, Hoffman E. La agricultura en Uruguay y su evolución. In: García Préchac F, Ernst O, Arbeletche P, Bidegain MP, Pritsch C, Ferenczi A, Rivas M, editores. Intensificación agrícola: oportunidades y amenazas para un país productivo y natural. Montevideo: Universidad de la República; 2010. pp. 13-27.
Aubriot L, Delbene L, Haakonson S, Somma A, Hirsch F, Bonilla S. Evolución de la eutrofización en el Río Santa Lucía: influencia de la intensificación productiva y perspectivas. Innotec. 2017;14:7-17. Doi: 10.26461/14.04.
Breiman L. Random forests. Machine learning. 2001;45:5-32.
Bridges CC. Hierarchical Cluster Analysis. Psychol Rep. 1966;18(3):851-4. Doi: 10.2466/pr0.1966.18.3.851.
Bu H, Meng W, Zhang Y, Wan J. Relationships between land use patterns and water quality in the Taizi River basin, China. Ecol Indic. 2014;41:187-97.
Caracterización de las cuencas del río San Salvador, río Yí Y río Arapey para fines de riego. Montevideo: MGAP; 2017. 198p.
CARU. Digesto sobre el uso y aprovechamiento del Río Uruguay [Internet]. Paysandú: CARU; 2019 [cited 2023 Oct 05]. 140p. Available from: https://bit.ly/3RRliBl
Centurion V, Fabre A, Kok P, Badano L, Neighbur N, Gelos M, Rodo E, Hoffmeister M, De Leon L. Evolución de la calidad de agua en la cuenca del río San Salvador: periodo 2014–2019. Montevideo: MVOTMV; 2020. 76p.
Ciganda V, Lizarralde C, Eguren G. Establecimiento de engorde a corral bovino o feedlots: cuantificación de su impacto sobre los recursos suelo y agua. Revista INIA. 2015;(41):39-44.
Cross T, Sathaye K, Darnell K, Niederhut D, Crifasi K. Predicting water production in the Williston basin using a machine learning model. In: Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, Virtual, 20–22 July 2020. [place unknown: publisher unknown]; 2020. pp. 3492–503. Doi: 10.15530/urtec-2020-2756.
De la Fuente E, Suárez SA. Problemas ambientales asociados a la actividad humana: la agricultura. Ecol Austral. 2008;18:239-52.
ESA. Sentinel-2 Mission Guide [Internet]. [place unknown]: ESA; [date unknown; cited 2023 Oct 05]. Available from: https://sentinels.copernicus.eu/web/sentinel/missions/sentinel-2
Fisher B, Turner RK, Morling P. Defining and classifying ecosystem services for decision making. Ecol Econ. 2009;68:643-53.
Frazier A. Landscape Metrics. In: Wilson JP, editor.The geographic information science & technology: body of knowledge. 2nd ed. [place unknown]: University Consortium for Geographic Information Science; 2019. Doi: 10.22224/gistbok/2019.2.3.
García AR, Fleite SN, Ciapparelli I, Vázquez Pugliese D, Weigandt C, Fabrizio de Iorio A. Observaciones, desafíos y oportunidades en el manejo de efluentes de feedlot en la provinicia de Buenos Aires, Argentina. Ecol Austral. 2015;25(3):255-62.
Ghazaryan G, Dubovyk O, Löw F, Lavreniuk M, Kolotii A, Schellberg J, Kussul N. A rule-based approach for crop identification using multi-temporal and multi-sensor phenological metrics. Eur J Remote Sens. 2018;51(1):511-24.
Google. Google Earth Engine [Internet]. Mountain View: Google; [date unknown; cited 2023 Oct 05]. Available from: https://earthengine.google.com/
Google Colab [Internet]. Mountain View: Google; 2023 [cited 2023 Oct 05]. Available from: https://colab.research.google.com/
Gorgoglione A, Gregorio J, Ríos A, Alonso J, Chreties C, Fossati M. Influence of land use/land cover on surface-water quality of Santa Lucía River, Uruguay. Sustainability. 2020;12(11):4692. Doi: 10.3390/su12114692.
Hammer Ø, Harper DA, Ryan PD. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron [Internet]. 2001 [cited 2023 Oct 05];4(1):9p. Available from: https://palaeo-electronica.org/2001_1/past/past.pdf
Hesselbarth MHK, Sciaini M, With KA, Wiegand K, Nowosad J. Landscape metrics: an open‐source R tool to calculate landscape metrics. Ecography. 2019;42(10):1648-57.
Horning N. Land cover classification methods [Internet]. Version 1.0. New York: American Museum of Natural History;2004 [cited 2023 Oct 05]. Available from: https://www.amnh.org/content/download/74344/1391366/file/land-cover-classification-methods.pdf
Huang C, Kim S, Song K, Townshed JRG, Davis P, Altstatt A, Rodas O, Yanosky A, Clay R, Tucker CJ, Musinsky J. Assessment of Paraguay’s forest cover change using landsat observations. Glob Planet Change. 2009;67:1-12. Doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2008.12.009.
IDEUY: Infraestructura de Datos Espaciales [Internet]. Montevideo: Uruguay Presidencia; [date unknown; cited 2023 Oct 05]. Available from: https://visualizador.ide.uy/ideuy/core/load_public_project/ideuy/
Jain AK. Data clustering: 50 years beyond K-means. Pattern Recognit Lett. 2010;31(8):651-66.
Jiang Z, Huete A, Didan K, Miura T. Development of a two-band enhanced vegetation index without a blue band. Remote Sens Environ. 2008;112(10):3833-45.
Kearns FR, Kelly NM, Carter JL, Resh VH. A method for the use of landscape metrics in freshwater research and management. Landsc Ecol. 2005;20:113-25.
Lee SW, Hwang SJ, Lee SB, Hwang HS, Sung HC. Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landsc Urban Plan. 2009;92(2):80-9.
Lintern A, Webb JA, Ryu D, Liu S, Bende-Michl U, Waters D, Leahy P, Wilson P, Western AW. Key factors influencing differences in stream water quality across space. WIREs Water. 2018;5:e1260. Doi: 10.1002/wat2.1260.
Liu A, Duodu GO, Goonetilleke A, Ayoko GA. Influence of land use configurations on river sediment pollution. Environ Pollut. 2017;229:639-46.
Lundberg SM, Lee SI. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions. In: Guyon I, Luxburg UV, Bengio S, Wallach H, Fergus R, Vishwanathan S, Garnett R, editors. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30. New York: NIPS; 2017. pp. 4765-74.
Maaten L van der, Hinton G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J Mach Learn Res. 2008;9:2579-605.
McGarigal K, Marks BJ. FRAGSTATS: spatial pattern analysis program for quantifying landscape structure. Portland: USDA; 1995. 122p.
Melgar R, Vitti G, De Melo V. Soja en Latinoamérica: fertilizando para altos rendimientos. IIP Boletín. 2011;20:81p.
Ministerio de Ambiente, OAN (UY). Observatorio Ambiental Nacional [Internet]. Montevideo: MA; [date unknown; cited 2023 Oct 05]. Available from: https://www.ambiente.gub.uy/oan/
Ministerio de Ganadería, Agricultura y Pesca (UY). Mapa integrado de cobertura/uso del suelo del Uruguay año 2018 [Internet]. Montevideo: MGAP; 2019 [cited 2023 Oct 05]. Available from: https://bit.ly/3rDrVN0
Ministerio de Ganadería, Agricultura y Pesca, DGRN (UY). Actualización de cobertura y uso del suelo del Uruguay al año 2020/2021 [Internet].Montevideo: MGAP; 2021[cited 2023 Oct 05]. Available from: https://bit.ly/45z8kM9
Mon R, Irurtia C, Botta G, Pozzolo O, Bellora F, Rivero D, Bomben M. Effects of supplementary irrigation on chemical and physical soil properties in the rolling pampa region of Argentina. Cienc Investig Agrar. 2007;34(3):187-94.
Monteiro MIC, Ferreira FN, De Oliveira NMM, Avila AK. Simplified version of the sodium salicylate method for analysis of nitrate in drinking waters. Anal Chim Acta. 2003;477(1):125-9.
Paruelo JM, Guerschman JP, Piñeiro G, Jobbágy EG, Verón SR, Baldi G, Baeza S. Cambios en el uso de la tierra en Argentina y Uruguay: marcos conceptuales para su análisis. Agrociencia. 2006;10(2):47-61. Doi: 10.31285/AGRO.10.929.
Pedregosa F, Varoquaux G, Gramfort A, Michel V, Thirion B, Grisel O, Blondel M, Prettenhofer P, Weiss R, Dubourg V, Vanderplas J, Passos A, Cournapeau D, Brucher M, Perrot M, Duchesnay E. Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. J Mach Learn Res. 2011;12:2825–30.
Plan de monitoreo río San Salvador:informe de actividades y presentación de resultados: 2015. Montevideo: MVOTMA; 2016. 67p.
Russo C, Castro A, Gioia A, Iacobellis V, Gorgoglione A. A Stormwater management framework for predicting first flush intensity and quantifying its influential factors. Water Resour Manag. 2023;37:1437-59.
Russo C, Castro A, Gioia A, Iacobellis V, Gorgoglione A. Improving the sediment and nutrient first-flush prediction and ranking its influencing factors: an integrated machine-learning framework. J Hydrol. 2023;616:128842. Doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128842.
Shapley LS. A value for n-person games. In: Kuhn H, Tucker A, editors. Contributions to the Theory of Games. Vol 2. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1953. pp. 307-17.
Sharma A, Mishra PK. State-of-the-art in performance metrics and future directions for data science algorithms. J Sci Res. 2020;64(2):221-38. Doi: 10.37398/JSR.2020.640232.
Shi ZH, Ai L, Li X, Huang XD, Wu GL, Liao W. Partial least-squares regression for linking land-cover patterns to soil erosion and sediment yield in watersheds. J Hydrol. 2013;498:165-76.
Standard methods: for examination of water and wastewater. 15th ed. Washington: APHA; 1995. 1134p.
Tomic O, Graff T, Liland KH, Naes T. Hoggorm: a python library for explorative multivariate statistics. J Open Source Softw. 2019;4(39):980. Doi: 10.21105/joss.00980.
Uuemaa E, Roosaare J, Mander Ü. Landscape metrics as indicators of river water quality at catchment scale. Hydrol Res. 2007;38(2):125-38.
Uuemaa E, Roosaare J, Mander Ü. Scale dependence of landscape metrics and their indicatory value for nutrient and organic matter losses from catchments. Ecol Indic. 2005;5(4):350-69.
Van Opstal NV, Caviglia OP, Melchiori RJM. Water and solar radiation productivity of double-crops in a humid temperate area. Aust J Crop Sci. 2011;5(13):1760-6.
Vilaseca F, Castro A, Chreties C, Gorgoglione A. Daily rainfall-runoff modeling at watershed scale: a comparison between physically-based and data-driven models. In: Gervasi O, Murgante B, Misra S, Garau C, Blečić I, Taniar D, Apduhan BO, Rocha AMAC, Tarantino E, Torre CM, editors. Computational Science and Its Applications: ICCSA 2021. Cham: Springer; 2021. pp. 18-33.
Wang J, Bao W, Gao Q, Si W, Sun Y. Coupling the Xinanjiang model and wavelet-based random forests method for improved daily streamflow simulation. J Hydroinformatics. 2021;23:589-604.
Withers PJ, Neal C, Jarvie HP, Doody DG. Agriculture and eutrophication: where do we go from here? Sustainability. 2014;6:5853-75. Doi: 10.3390/su6095853.
Xu S, Li SL, Zhong J, Li C. Spatial scale effects of the variable relationships between landscape pattern and water quality: example from an agricultural karst river basin, Southwestern China. Water Resour Manag. 2020;300:106999. Doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2020.106999.
Zhong S, Zhang K, Wang D, Zhang H. Shedding light on ‘‘Black Box’’ machinelearning models for predicting the reactivity of HO radicals toward organic compounds. Chem Eng J. 2021;405:126627. Doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126627.
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2023 Agrociencia Uruguay

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
| Estadísticas de artículo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas de resúmenes | |
| Vistas de PDF | |
| Descargas de PDF | |
| Vistas de HTML | |
| Otras vistas | |















