Fixed environmental effects and connectedness of the genetic evaluation of the Limousin breed in Uruguay
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31285/AGRO.24.141Keywords:
Limousin, environmental effects, genetic connectedness, UruguayAbstract
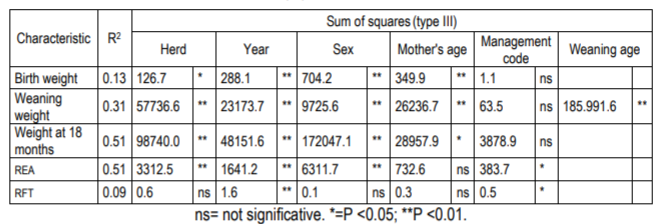
Genetic evaluations are an efficient tool to select sires, and for them it is necessary to have identification of environmental effects, genetic parameters, and acceptable degree of connectedness between herds. Evaluation of Limousin breed genetics has been developing since 2012. The objectives were to determine the most relevant fixed environmental effects of the characteristics in the genetic evaluation and to estimate the degree of connectedness between herds. The productive and genealogical records were extracted from the Limousin genetic evaluation database of the National Institute of Agricultural Research. Objective measurements were available for the characteristics birth weight (916 records), weaning (818), 18 months (438), ribeye area (435), and 12th-13th rib fat thickness (435) for 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015 and 2016 corresponding to four herds. The results showed that the fixed environmental effects considered presented a significant value (p<0.05), and that herds were connected to each other with average values of prediction error variance (pevd), and connectedness rating (cr) of 113.9 and 7.9, respectively. Concluding that the most relevant fixed environmental effects were year, sex, herd, age at weaning and age at 18 months, and that herds were connected with a low connectedness degree.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |

















