Efeito da aplicação de efluentes de tambo crus e estabilizados na fertilidade do solo e riscos sanitários associados
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31285/AGRO.28.1184Palavras-chave:
aplicação de efluente leiteiro, bactérias indicadoras de patógenos, fertilidade do solo, genes de resistência antimicrobiana, biomassa vegetalResumo
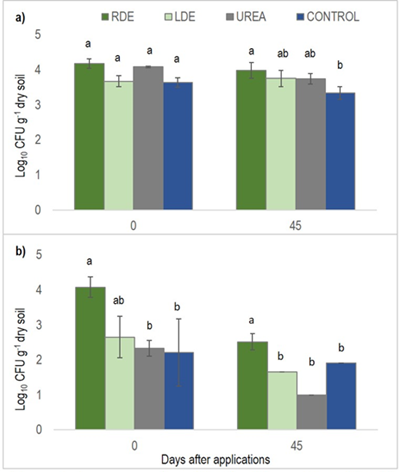
A intensificação da produção leiteira em Uruguai gera grandes volumes de resíduos orgânicos de difícil manejo e com potenciais riscos à saúde. A irrigação de efluentes de tambo (DE) é uma prática agrícola recomendada para melhorar a fertilidade do solo. O objetivo deste trabalho foi avaliar a aplicação em Festuca arundinacea de DE bruto (RDE) e estabilizada em dois lagoas (LDE) comparada à adubação com ureia sobre o teor de nutrientes do solo e planta, indicadores de bactérias patogênicas e a persistência de alguns genes de resistência antimicrobiana. Em estufa, foram feitas quatro aplicações sazonais com dose total equivalente a 200 kg N há-1. O teor de Na do solo aumentou após as aplicações de DE. A aplicação de DE não aumentou o teor de nutrientes da festuca. A persistência de E. coli foi baixa, mas foi detectada com RDE. Os genes beta-lactâmicos blaTEM e blaOXA foram detectados em ambos os DE, mais em LDE, mas não foram detectados no solo. A aplicação de DE mostrou efeitos comparáveis aos do controle e da uréia no teor de nutrientes da festuca e modificou ligeiramente química do solo. LDE reduzem a carga de bactérias patogênicas e destaca a segurança de sua aplicação.
Downloads
Referências
Alef K. Soil respiration. In: Alef K, Nannipieri P, editors. Methods in Applied Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry. Londres: Elsevier; 1995. p. 193-270.
Avery LM, Killham K, Jones DL. Survival of E. coli O157: H7 in organic wastes destined for land application. J Appl Microbiol. 2005;98(4):814-22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02524.x
Barkle GF, Stenger R, Singleton PL, Painter DJ. Effect of regular irrigation with dairy farm effluent on soil organic matter and soil microbial biomass. Aust J Soil Res. 2000;38(6):1087-97. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1071/SR99127
Bhogal A, Nicholson FA, Rollett A, Taylor M, Litterick A, Whittingham MJ, Williams JR. Improvements in the quality of agricultural soils following organic material additions depend on both the quantity and quality of the materials applied. Front Sustain Food Syst. 2018;2:9. Doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2018.00009. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2018.00009
Bolan NS, Horne DJ, Currie LD. Growth and chemical composition of legume‐based pasture irrigated with dairy farm effluent. N Z J Agric Res. 2004;47(1):85-93. Doi: 10.1080/00288233.2004.9513574. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00288233.2004.9513574
Bolan NS, Laurenson S, Luo J, Sukias J. Integrated treatment of farm effluents in New Zealand’s dairy operations. Bioresour Technol. 2009;100(22):5490-7. Doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.03.004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.03.004
Bray RH, Kurtz LT. Determination of total, organic, and available forms of Phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci. 1945;59(1):39-46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-194501000-00006
Bremner JM, Mulvaney CS. Total nitrogen. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney D, editors. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2. Madison: American Society of Agronomy; 1996. p. 595-624.
Carvalho IT, Santos L. Antibiotics in the aquatic environments: a review of the European scenario. Environ Int. 2016;94:736-57. Doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2016.06.025. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.06.025
Chen QL, An XL, Li H, Zhu YG, Su JQ, Cui L. Do manure-borne or indigenous soil microorganisms influence the spread of antibiotic resistance genes in manured soil? Soil Biol Biochem. 2017;114:229-37. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.07.022
Coban H, Miltner A, Elling FJ, Hinrichs KU, Kästner M. The contribution of biogas residues to soil organic matter formation and CO2 emissions in an arable soil. Soil Biol Biochem. 2015;86:108-15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.03.023
Correa C, Rezzano N, García F. Manual para la gestión ambiental de tambos [Internet]. Montevideo: LATU; 2016 [cited 2024 Feb 23]. 83p. Available from: https://bit.ly/42RRurY
Dallenne C, Da Costa A, Decré D, Favier C, Arlet G. Development of a set of multiplex PCR assays for the detection of genes encoding important beta-lactamases in Enterobacteriaceae. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010;65(3):490-5. Doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp498. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkp498
Demanet R, Aguilera M, Mora M. Efecto de la aplicación de purines sobre el sistema suelo-planta. Front Agrícola [Internet]. 1999 [cited 2024 Feb 22];5:87-94. Available from: https://repositorio.uchile.cl/handle/2250/121498
Di Rienzo JA, Casanoves F, Balzarini MG, González L, Tablada M, Robledo YC. InfoStat. Versión 2020 [Internet]. Córdoba: Universidad Nacional de Córdoba; 2017 [cited 2024 Feb 22]. Available from: http://www.infostat.com.ar
Dungan RS, McKinney CW, Leytem AB. Tracking antibiotic resistance genes in soil irrigated with dairy wastewater. Sci Total Environ. 2018;635:1477-83. Ddoi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.020. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.020
Fariña SR, Chilibroste P. Opportunities and challenges for the growth of milk production from pasture: the case of farm systems in Uruguay. Agric Syst. 2019;176:102631. Doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2019.05.001. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2019.05.001
Fortunato G, Vaz-Moreira I, Becerra-Castro C, Nunes OC, Manaia CM. A rationale for the high limits of quantification of antibiotic resistance genes in soil. Environ Pollut. 2018;243(Pt B):1696-703. Doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.128. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.09.128
Fyfe J, Hagare D, Sivakumar M. Dairy shed effluent treatment and recycling: effluent characteristics and performance. J Environ Manage. 2016;180:133-46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.04.058
Gianneechini R, Concha C, Delucci I, Gil J, Salvarrey L, Rivero R. Mastitis bovina, reconocimiento de los patógenos y su resistencia antimicrobiana en la Cuenca Lechera del Sur de Uruguay. Veterinaria (Montevideo). 2014;50(196):4-32.
Gianneechini RE, Concha C, Franklin A. Antimicrobial susceptibility of udder pathogens isolated from dairy herds in the west littoral region of Uruguay. Acta Vet Scand. 2002;43(1):31-41. Doi: 10.1186/1751-0147-43-31. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1751-0147-43-31
Gianneechini RE, Concha C, Riveroj R, Gil J, Moreno-Lopez J. Monitoreo de la resistencia de Staphylococcus aureus aislados en rodeos lecheros de la cuenca lechera tradicional de Uruguay. In: XXXIII jornadas Uruguayas de Buiatría. Paysandú: Centro Médico Veterinario de Paysandú; 2005. p. 205-7.
Goulding KWT. Soil acidification and the importance of liming agricultural soils with particular reference to the United Kingdom. Soil Use Manag. 2016;32(3):390-9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/sum.12270
Gutiérrez S, Cabrera N, Benítez A, Melani E. Reducing variability in estimating wastewater composition in dairy farms during milking operations. Biosyst Eng. 2009;103(4):497-503. Doi: 10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2009.06.004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2009.06.004
Hawke RM, Summers SA. Effects of land application of farm dairy effluent on soil properties: a literature review. N Z J Agric Res. 2006;49(3):307-20. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00288233.2006.9513721
Hawke RM, Summers SA. Land application of farm dairy effluent: Results from a case study, wairarapa, New Zealand. N Z J Agric Res. 2003;46(4):339-46. Doi: 10.1071/SR99127. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00288233.2003.9513562
Helt CD, Weber KP, Legge RL, Slawson RM. Antibiotic resistance profiles of representative wetland bacteria and faecal indicators following ciprofloxacin exposure in lab-scale constructed mesocosms. Ecol Eng. 2012;39:113-22. Doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.11.007. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2011.11.007
Herrero MA, Palhares JCP, Salazar FJ, Charlón V, Tieri MP, Pereyra AM. Dairy manure management perceptions and needs in South American countries. Front Sustain Food Syst. 2018;2:22. Doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2018.00022. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2018.00022
Illarze G, del Pino A, Rodríguez-Blanco A, Irisarri P. application of dairy effluents to pastures affects soil nitrogen dynamics and microbial activity. Agronomy. 2023;13(2):470. Doi: 10.3390/agronomy13020470. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13020470
Isaac RA, Kerber JD. Atomic absorption and flame photometry: techniques and uses in soil, plant, and water analysis. In: Walsh LM, editor. Instrumental Methods for Analysis of Soils and Plant Tissue. Madison: SSSA; 1971. p. 17-37. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2136/1971.instrumentalmethods.c2
Jang J, Hur HG, Sadowsky MJ, Byappanahalli MN, Yan T, Ishii S. Environmental Escherichia coli: ecology and public health implications: a review. J Appl Microbiol. 2017;123(3):570-81. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13468
La Manna A, Mieres J, Acosta Y, Torres I. Utilización de efluentes en tambos: resumen de Investigación. In: Resultados experimentales en lechería. Montevideo: INIA; 2004. p. 35-44.
Liu M, Hu F, Chen X, Huang Q, Jiao J, Zhang B, Li H. Organic amendments with reduced chemical fertilizer promote soil microbial development and nutrient availability in a subtropical paddy field: the influence of quantity, type and application time of organic amendments. Appl Soil Ecol. 2009;42(2):166-75. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2009.03.006
Liu P, Jia S, He X, Zhang X, Ye L. Different impacts of manure and chemical fertilizers on bacterial community structure and antibiotic resistance genes in arable soils. Chemosphere. 2017;188:455-64. Doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.162. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.162
Liu YY, Haynes RJ. Long-term irrigation with dairy factory wastewater influences soil quality. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology. 2010;4:524-8.
Manshadi FD, Karpiscak M, Gerba CP. Enteric bacterial contamination and survival on produce during irrigation with dairy wastewater in the field. Water Reuse. 2013;3(2):102-10. Doi: 10.2166/wrd.2013.161. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2013.161
McKinney CW, Dungan RS, Moore A, Leytem AB. Occurrence and abundance of antibiotic resistance genes in agricultural soil receiving dairy manure. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2018;94(3). Doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiy010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiy010
Monaghan RM, Hedley MJ, Di HJ, McDowell RW, Cameron KC, Ledgard SF. Nutrient management in New Zealand pastures-recent developments and future issues. N Z J Agric Res. 2007;50(2):181-201. Doi: 10.1080/00288230709510290. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00288230709510290
Monaghan RM, Houlbrooke DJ, Smith LC. The use of low-rate sprinkler application systems for applying farm dairy effluent land to reduce contaminant transfers. N Z J Agric Res. 2010;53(4):389-402. Doi: 10.1080/00288233.2010.505943. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00288233.2010.505943
Murphy J, Riley JP. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal Chim Acta. 1962;27(C):31-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
Nõlvak H, Truu M, Kanger K, Tampere M, Espenberg M, Loit E, Raave H, Truu J. Inorganic and organic fertilizers impact the abundance and proportion of antibiotic resistance and integron-integrase genes in agricultural grassland soil. Sci Total Environ. 2016;562:678-89. Doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.035. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.035
Öhlinger R. Soil respiration by tritation. In: Schinner F, Öhlinger R, Kandeler E, Margesin R, editors. Methodsinsoil biology. New York: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 1996. p. 95-8.
Pachepsky YA, Sadeghi AM, Bradford SA, Shelton DR, Guber AK, Dao T. Transport and fate of manure-borne pathogens: modeling perspective. Agric Water Manag. 2006;86(1-2):81-92. Doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2006.06.010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2006.06.010
Peak N, Knapp CW, Yang RK, Hanfelt MM, Smith MS, Aga DS, Graham DW. Abundance of six tetracycline resistance genes in wastewater lagoons at cattle feedlots with different antibiotic use strategies. Environ Microbiol. 2007;9(1):143-51. Doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01123.x. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01123.x
Prado J, Ribeiro H, Alvarenga P, Fangueiro D. A step towards the production of manure-based fertilizers: Disclosing the effects of animal species and slurry treatment on their nutrients content and availability. J Clean Prod. 2022;337:130369. Doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130369. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130369
Roach CG, Longhurst RD, Ledgard SF. Land application of farm dairy effluent for sustainable dairy farming. Proc New Zeal Grassl Assoc. 2001;(63):53-7. Doi: 10.33584/jnzg.2001.63.2430. DOI: https://doi.org/10.33584/jnzg.2001.63.2430
Saunders OE, Fortuna AM, Harrison JH, Whitefield E, Cogger CG, Kennedy AC, Bary AI. Comparison of Raw Dairy Manure Slurry and Anaerobically Digested Slurry as N Sources for Grass Forage Production. Int J Agron. 2012;2012:101074. Doi: 10.1155/2012/101074. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/101074
Schages L, Wichern F, Kalscheuer R, Bockmühl D. Winter is coming - Impact of temperature on the variation of beta-lactamase and mcr genes in a wastewater treatment plant. Sci Total Environ. 2020;712:136499. Doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136499. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136499
Spiehs M, Goyal S. Best management practices for pathogen control in manure management systems. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota; 2007. 10p.
Sukias JPS, Tanner CC, Davies-Colley RJ, Nagels JW, Wolters R. Algal abundance, organic matter, and physico-chemical characteristics of dairy farm facultative ponds: implications for treatment performance. N Z J Agric Res. 2001;44(4):279-96. Doi: 10.1080/00288233.2001.9513485. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/00288233.2001.9513485
Thomas G. Exchangeable cations. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney D, editors. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2. Madison: American Society of Agronomy; 1982. p. 159-65. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2134/agronmonogr9.2.2ed.c9
Wang XM, Di HJ, Cameron KC, Li B. Effect of treated farm dairy effluent on E. coli, phosphorus and nitrogen leaching and greenhouse gas emissions: a field lysimeter study. J Soils Sediments. 2019;19(5):2303-12. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-02228-9
Zibilske LM. Carbon mineralization. In: Weaver R, Angle S, Bottomley P, Bezdicek D, Smith S, Tabatabai A, Wollum A, editors. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Microbiological and Biochemical Properties. Madison: American Society of Agronomy; 1994. p. 835-63.
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2024 Agrociencia Uruguay

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
| Métricas do artigo | |
|---|---|
| Vistas abstratas | |
| Visualizações da cozinha | |
| Visualizações de PDF | |
| Visualizações em HTML | |
| Outras visualizações | |















